Early childhood education is vital for a child’s future, influencing cognitive, emotional, and social development. This article discusses effective strategies like play-based learning, social-emotional development, and parental involvement, emphasizing their benefits for young children.
The Importance of Early Childhood Education
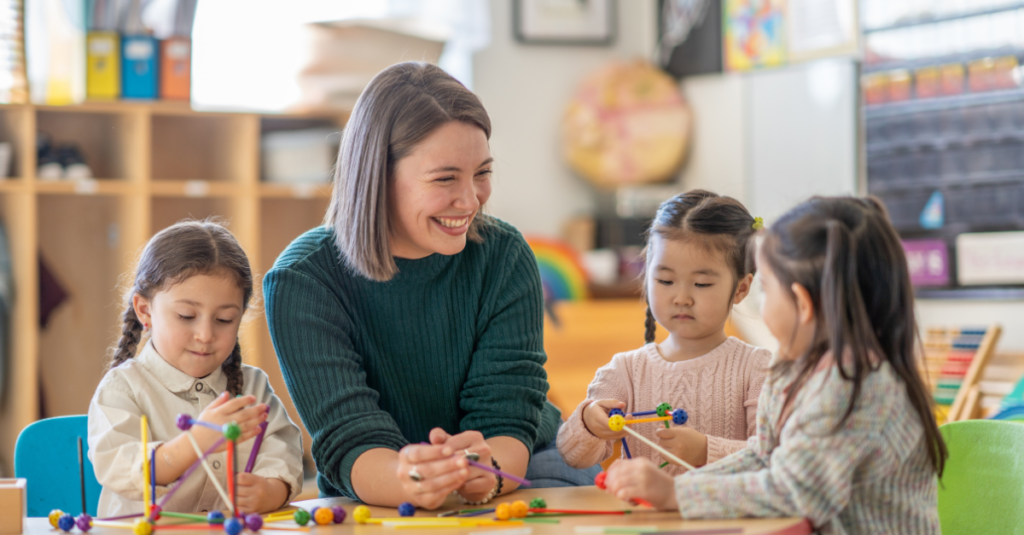
The first few years of a child’s life are characterized by rapid brain development, making it a critical period for learning and growth. Early childhood education provides a structured environment where children can develop essential skills, including language, motor skills, and social interactions. Research shows that children who participate in high-quality early education programs are more likely to succeed academically, socially, and emotionally later in life. Therefore, investing in early childhood education is not only beneficial for individual children but also for society as a whole.
Key Strategies for Fostering Growth and Development
Play-Based Learning
Play-based learning is a fundamental strategy in early childhood education. Through play, children explore their environment, develop creativity, and enhance problem-solving skills. Play-based learning encourages active engagement, allowing children to learn at their own pace and in ways that are meaningful to them. Activities such as building blocks, role-playing games, and interactive story sessions provide opportunities for hands-on learning and cognitive development.
Social-Emotional Development
Fostering social-emotional development is essential for nurturing well-rounded individuals. Early childhood education programs should focus on helping children build healthy relationships, manage emotions, and develop empathy. Activities that promote teamwork, cooperation, and communication are vital for social-emotional growth. Educators can create a supportive environment by encouraging positive interactions and teaching conflict resolution skills. Programs like Second Step and PATHS (Promoting Alternative Thinking Strategies) have been successful in enhancing social-emotional competencies in young children.
Parental Involvement
Parental involvement is a cornerstone of effective early childhood education. When parents actively engage in their child’s learning process, it reinforces the skills and concepts taught in educational settings. Parents can support learning at home by reading to their children, engaging in educational activities, and maintaining open communication with educators. Daycare like those available in Farmington can facilitate parental involvement by organizing workshops, parent-teacher conferences, and family engagement events. Studies indicate that children with involved parents are more likely to excel academically and exhibit positive behavior.
Benefits of These Strategies
Cognitive Development
Play-based learning stimulates cognitive development by encouraging exploration and curiosity. Activities that challenge young minds help build critical thinking and problem-solving skills. For example, puzzle-solving enhances spatial awareness and logical reasoning, while storytelling fosters language development and imagination.
Emotional Development
Social-emotional development strategies help children understand and manage their emotions. By learning to express their feelings and empathize with others, children develop emotional intelligence, which is crucial for building healthy relationships and coping with life’s challenges. Programs that focus on social-emotional learning have been shown to reduce behavior problems and improve academic performance.
Social Development
Interacting with peers and adults in a structured environment helps children develop social skills. Play-based activities and group projects teach children how to collaborate, share, and communicate effectively. These skills are essential for success in school and beyond. Early childhood education programs that prioritize social development create a foundation for lifelong interpersonal skills.
Practical Tips for Educators and Parents
- Create a Stimulating Environment: Design learning spaces that encourage exploration and creativity. Use a variety of materials and resources to cater to different learning styles.
- Encourage Play: Integrate play-based activities into daily routines. Allow children to lead their play and provide opportunities for imaginative and cooperative play.
- Support Emotional Learning: Teach children to recognize and express their emotions. Use stories, role-playing, and discussions to explore feelings and develop empathy.
- Engage Parents: Foster strong partnerships with parents by keeping them informed about their child’s progress and involving them in educational activities. Provide resources and guidance for supporting learning at home.
Conclusion
Effective early childhood education strategies, like play-based learning, social-emotional development, and parental involvement, are crucial for nurturing young children’s growth. These approaches lay a strong foundation for cognitive, emotional, and social development, paving the way for lifelong success. By adopting these strategies and supporting early education initiatives, we can help every child thrive and reach their full potential.