Bone grafting in dental care is a fascinating blend of art and science, crucial for many oral health treatments. Understanding when and why bone grafting is needed can help patients feel more comfortable with the process. This blog post will explore the fundamentals of bone grafting, providing insights into the procedure and what to expect, making complex dental care concepts easily digestible.
What is Bone Grafting?
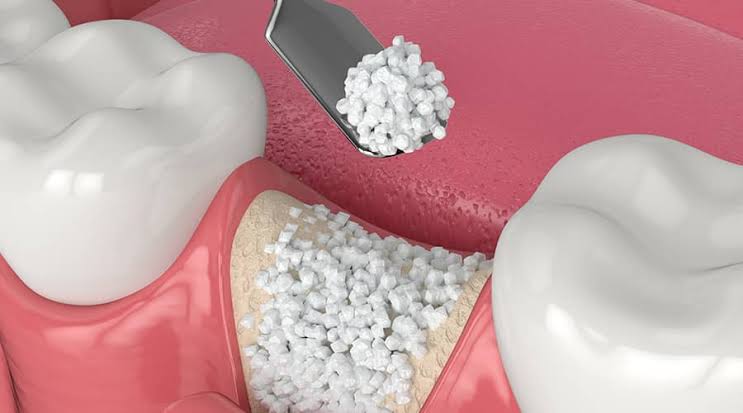
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing or damaged bone mass. In dentistry, it’s essential for maintaining jawbone health. The process involves transplanting bone tissue to repair and rebuild damaged bones, often in the jaw area. This procedure is vital for patients who have lost teeth or suffer from bone loss due to disease or trauma.
Bone grafting helps provide a stable foundation for dental implants, which rely on sufficient bone mass for support. Without adequate bone structure, implants may not fuse properly with the jawbone. Understanding this procedure can alleviate concerns about dental surgery, ensuring patients know they’re in good hands.
When is Bone Grafting Needed?
Bone grafting isn’t required for every patient, but it’s crucial in specific scenarios. One common necessity is when preparing for dental implants. If a patient has insufficient bone density, grafting ensures the implant can anchor securely to the jaw.
In addition, bone grafting is often necessary after tooth extraction, especially if the tooth has been missing for a while. Bone loss can occur in these situations, leading to changes in facial structure. By addressing bone loss early, patients can maintain their facial appearance and oral health.
Periodontal disease is another situation where bone grafting might be recommended. This condition can cause bone loss around natural teeth, and grafting helps restore the lost bone, supporting the remaining teeth and improving oral health.
Types of Bone Grafts
Several types of bone grafts exist, each serving a specific purpose. Autografts involve taking bone from the patient’s own body, usually from the chin or hip. This method is often considered the gold standard due to its compatibility and the absence of rejection risk.
Allografts use bone obtained from a donor, typically processed and sterilized to ensure safety. This method eliminates the need for a second surgical site, reducing recovery time.
Xenografts utilize bone from animals, usually cows. These grafts are processed to remove any potential allergens and are an excellent choice for patients who prefer not to undergo additional surgery for harvesting bone.
The Bone Grafting Procedure
When preparing for bone grafting, patients should understand what the procedure involves. Typically, the process begins with an X-ray to assess bone loss and plan the graft placement. An oral surgeon in Richmond, Indiana, for instance, will ensure you fully understand the steps before proceeding.
The surgery itself is performed under local anesthesia or sedation for comfort. The oral surgeon makes an incision in the gum to access the bone. The chosen graft material is then placed and secured, often with small screws or plates. Finally, the gums are stitched and allowed to heal.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from bone grafting is typically straightforward but requires some care. Patients may experience mild discomfort, swelling, or bruising, manageable with prescribed pain medication.
Following the surgeon’s aftercare instructions is crucial for successful healing. This includes maintaining oral hygiene, avoiding hard foods, and attending follow-up appointments. Recovery times vary, but most patients resume normal activities within a week.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, bone grafting has potential risks and complications. Infection, nerve damage, or graft rejection, though rare, can occur. Choosing a qualified and experienced oral surgeon minimizes these risks.
Patients should discuss their medical history with their surgeon to ensure the best outcome. Understanding the potential risks helps patients make informed decisions about their oral health care.
Benefits of Bone Grafting
Bone grafting provides numerous benefits for dental health. It strengthens the jawbone, supports dental implants, and facilitates better oral function. By restoring bone mass, patients can chew and speak more effectively, improving their overall quality of life.
Additionally, bone grafting can enhance facial aesthetics by maintaining the natural structure of the face. This is particularly important for patients with significant bone loss, as it can prevent the sunken appearance often associated with missing teeth.
Conclusion
Bone grafting is a valuable tool in modern dentistry, offering solutions for patients with bone loss or those preparing for dental implants. Understanding when and why bone grafting is needed, the procedure itself, and its benefits can empower patients to make informed decisions about their oral health.
For those considering bone grafting, consulting with an experienced oral surgeon in Richmond, Indiana, can provide personalized guidance and care. With the right approach, bone grafting can significantly enhance both dental function and aesthetics, contributing to improved overall well-being.