Decoding the Cricket Pitch: Construction, Characteristics, and Analysis

The cricket pitch serves as the stage where the battle between the bat and ball takes place. A cricket pitch is a well maintained area of ground that is essential to determining the result of a game. For players, coaches, and spectators, it is essential to comprehend every aspect of a cricket pitch, including its building method, characteristics, and analysis. The purpose of this article is to give a thorough explanation of these components while highlighting the intriguing realm of cricket pitch dynamics.
The major component of the game, the cricket pitch, often known as the “strip” or “wicket,” determines the pace and result of matches. Here, batsmen face off against the bowlers, spinners make use of turn, while fast bowlers produce pace and bounce. Understanding the subtleties of a cricket pitch is crucial for fully appreciating the sport’s complexities.
So first , we will delve into the key elements and characteristics of a cricket pitch, unraveling its mysteries and shedding light on its significance.
Dimensions and Layout

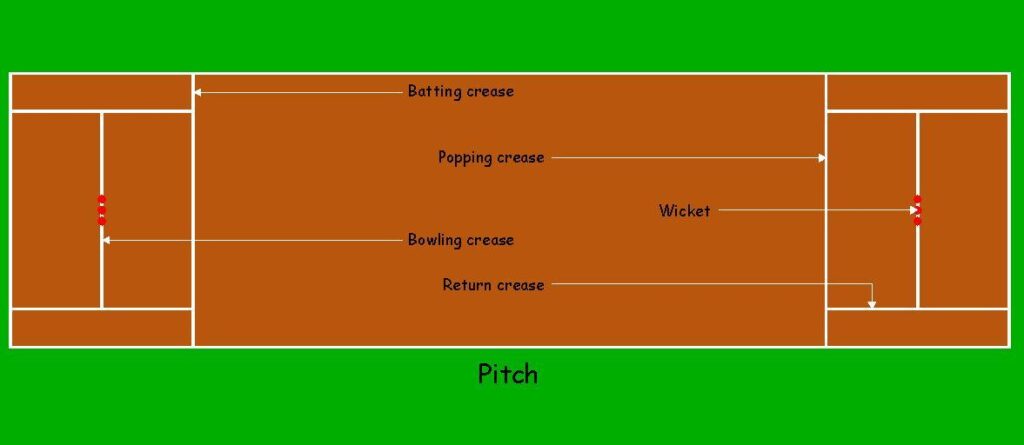
The center of the field is where the rectangular cricket pitch is located. Its length is 22 yards (20.12 meters), and the width is 10 feet (3.05 meters). The pitch is marked with white lines and has the following important markings:
Bowling Crease: At each end of the pitch, two parallel lines are drawn that are 8 feet 8 inches (2.64 meters) apart. These lines designate where the bowler will release the ball.
Popping Crease: At either end, two short lines parallel to the bowling crease are indicated. The batsmen’s safe zone while running between the wickets is indicated by these markers, which are typically 4 feet (1.22 meters) long.
Return Creases: Drawn at a right angle to the bowling crease, they are extensions of the popping crease. The start of the bowler’s run-up is indicated by the return creases.
Pitch Characteristics
Surface Composition
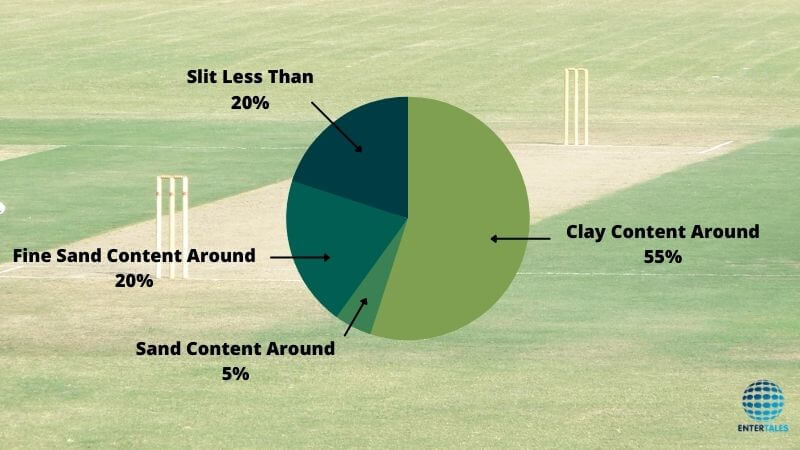
A cricket pitch typically consists of multiple layers, each of which affects the pitch’s behavior in substantial ways. Clay that has been compressed typically makes up the top layer, which gives spin bowlers their grip. The pitch is composed of a mix of loam, clay, and sandy soil beneath the clay layer, which encourages stability and good bounce.
Grass Cover
Gameplay is substantially impacted by the presence and length of grass on the field. Shorter grass favors hitters by allowing the ball to land on the bat more rapidly. Longer grass, on the other hand, can help fast bowlers by adding to their speed, movement, and seam grip.
Wear and Tear
The pitch experiences deterioration as a cricket match goes on, changing its qualities. Cracks may appear on the ground due to wear, which will change the bounce and benefit spin bowlers. The wear patterns also lead to varied bounce, which makes it difficult for batsmen to choose their shots.
Pitch Conditions
Pitch conditions are affected by numerous variables, including weather, soil moisture, and climate. Fast bowlers take advantage of the pitch becoming harder and faster under dry and hot weather. On the other hand, damp or moist circumstances can help swing bowlers by facilitating lateral movement.
Pitch Behaviour

Bounce
The height of the ball’s bounce after being pitched is referred to as the bounce of a cricket pitch. Pitches with constant bounce make it easier for players to judge and play strokes. However, inconsistent bounce or too much variation can make batting challenging and provide bowlers opportunities.
Turn
Spin bowlers rely on the ability of the pitch to generate turn. Turn refers to the sideways movement of the ball after pitching, and it plays a crucial role in deceiving batsmen. Pitches with sufficient grip and roughness can assist spinners in extracting turn and causing trouble for batsmen.
Pace and Seam Movement
Fast wickets with movement off the seam are ideal for fast bowlers. Fast bowlers can benefit from pitches with grass cover and mild dampness because they enable the ball to skid through or seam off the pitch more quickly.
Analysis for Cricket Pitch Construction
An extensive analysis is required to identify the site suitability, soil composition, and other critical elements before beginning the construction of a cricket pitch. The essential components of analysis include:
Site Selection:
Choosing the right site is essential for a level playing field. It evaluates elements like soil composition, drainage, sunlight exposure, and wind direction. The pitch should ideally be in the middle of the cricket field to ensure that both teams have an equal chance to play.
Soil testing:
Understanding the properties and suitability of the soil for a cricket pitch requires analysis of its composition. The site’s soil is sampled, and its texture, clay content, organic matter, and pH level are all examined. This analysis aids in determining the soil’s capacity for durability, bounce, and grip.
Climate and Weather Considerations:
When building a pitch, it is important to consider the regional climate and weather. To comprehend how they would affect the pitch’s behavior, factors like temperature, humidity, rainfall, and seasonal changes are taken into account. For instance, hot and dry weather may result in a surface that is harder and faster, favoring fast bowlers.
Grass Selection:
Different grass species are chosen for different pitches based on the desired playing attributes as well as wear tolerance, growth rate, and ball impact resistance. In order to improve the pitch’s evenness and stability, analysis is done on different grass varieties to find those that can cover the area well, control moisture levels, and perform all of these things.
Construction Process of a Cricket Pitch

After the groundwork of analysis has been laid, a cricket pitch can be built. A high-quality playing surface is the result of a multi-step procedure. Following are the main steps:
Site Preparation:
Preparing the Site entails removing any unwanted objects or plants from the designated area. The land has been leveled to remove any undulations or bumps and create a smooth surface. To avoid flooding, drains are provided if necessary.
Soil Preparation:
The soil is analyzed so that the right adjustments can be made to improve its structure and quality. To attain the desired soil qualities, it may be necessary to incorporate materials such as clay, loam, sand, or organic matter.
Pitch Dimensions:
The pitch is 22 yards long and 10 feet wide, and its dimensions have been chalked out. All legal creases, including the popping crease, bowling crease, and return crease, have been clearly delineated.
Clay Layer:
The area is then covered with a layer of clay-based soil, approximately 10-12 mm deep. The clay helps the surface last longer and gives spin bowlers more traction.
Rolling and Compaction:
Heavy machinery is used to roll the pitch, which compacts the clay layer and removes air spaces. This method guarantees a steady playing field, with less bouncing around and consistent behavior.
Grass Planting and Maintenance:
The clay is then seeded with specialized grass seeds chosen through the analysis. In order to get the ideal grass height, density, and playing characteristics, routine care procedures including mowing, watering, and fertilizing must be performed as the grass develops and establishes over time.
Pitch Monitoring
Pitch monitoring occurs during construction and matches. Its bounce, wear, and weather response are evaluated. Maintaining the pitch’s integrity and fairness may need adjustments.
Conclusion
Cricket pitch architecture, analysis, and characteristics reveal game dynamics. The pitch’s careful construction, maintenance, and analysis assure fair play between batsmen and bowlers, adding to cricket’s thrill and challenge. Players and fans can better understand this exciting sport’s methods, talents, and tactics by understanding the cricket pitch.
Swikriti Dandotia




